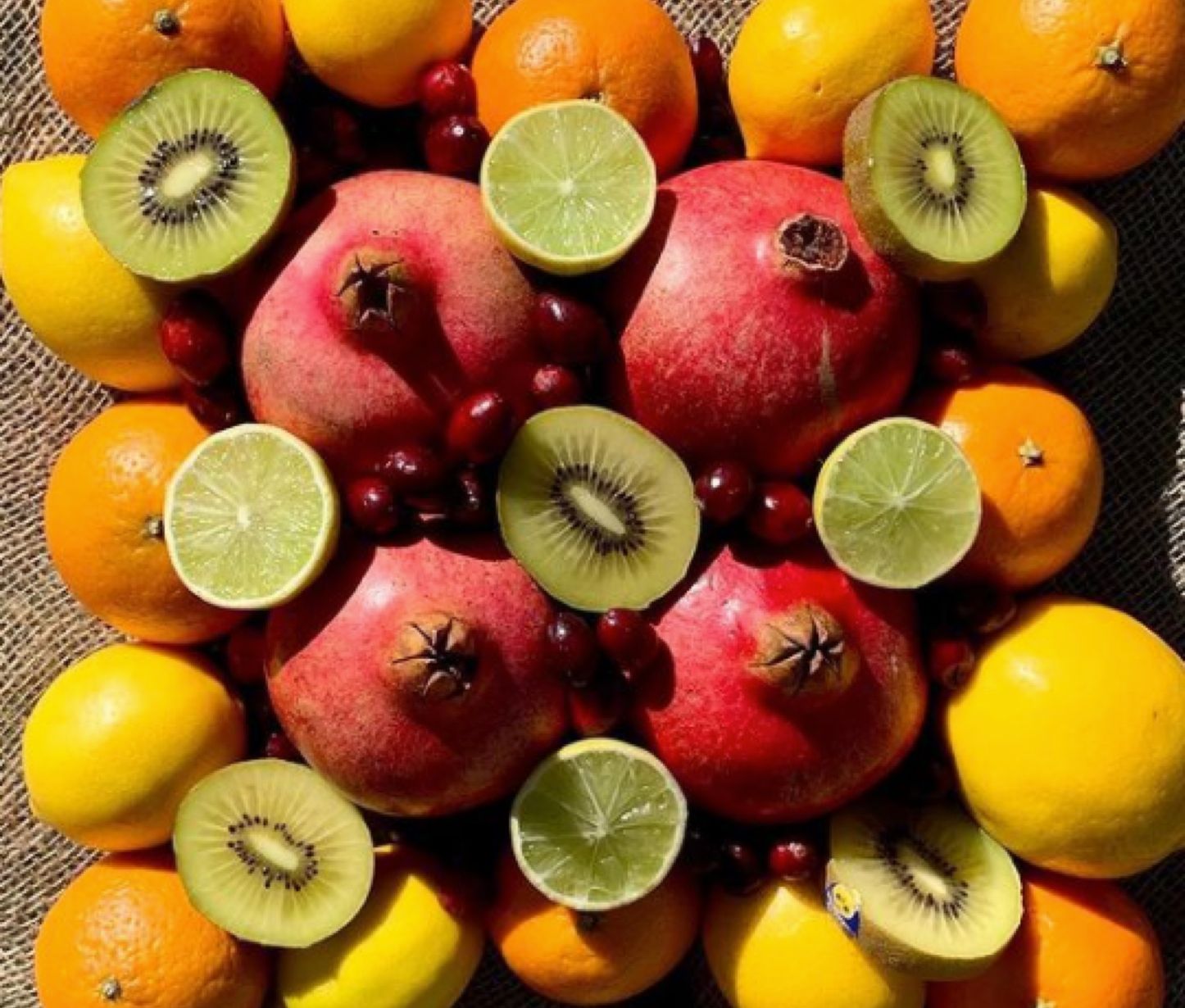
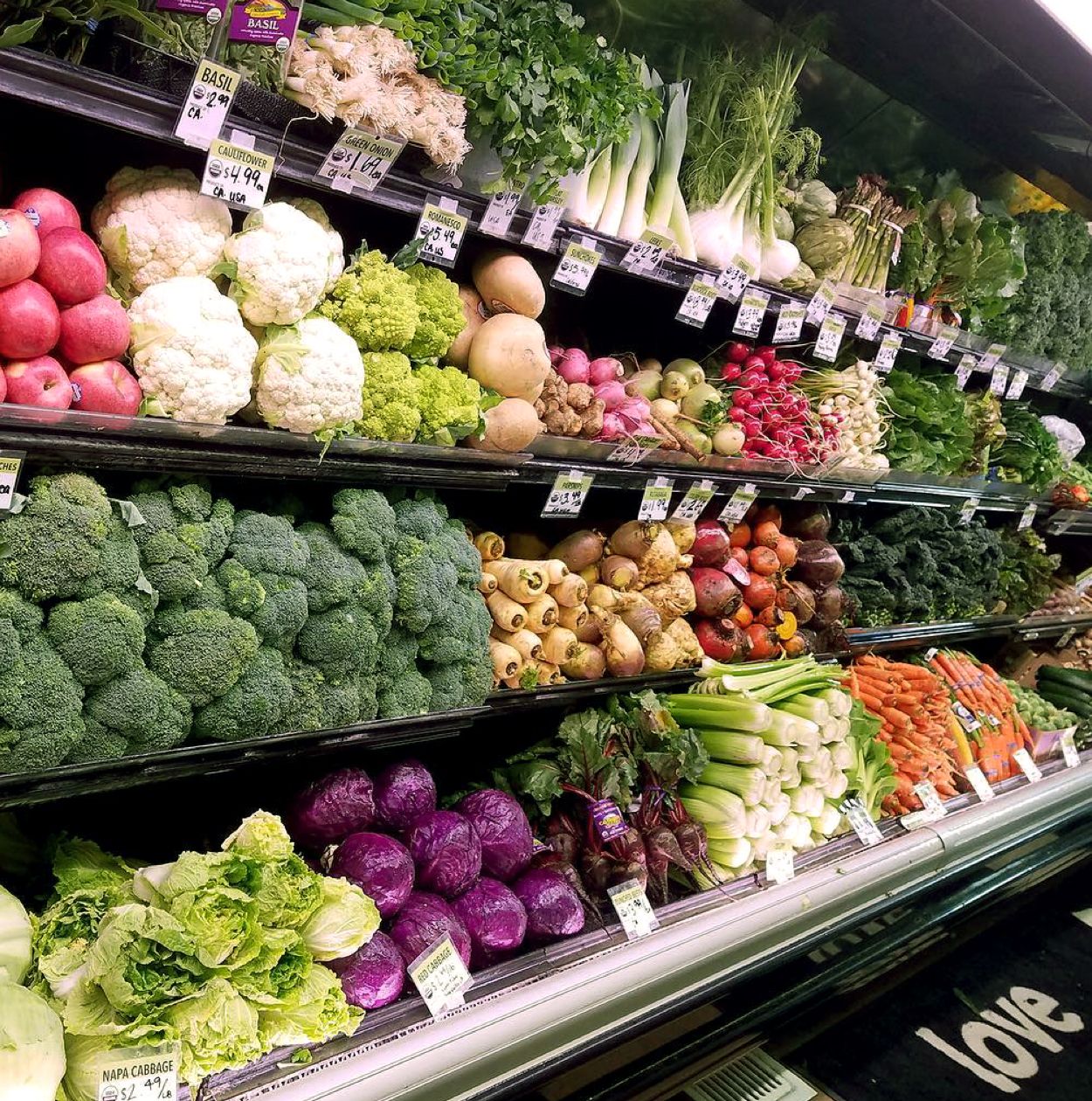
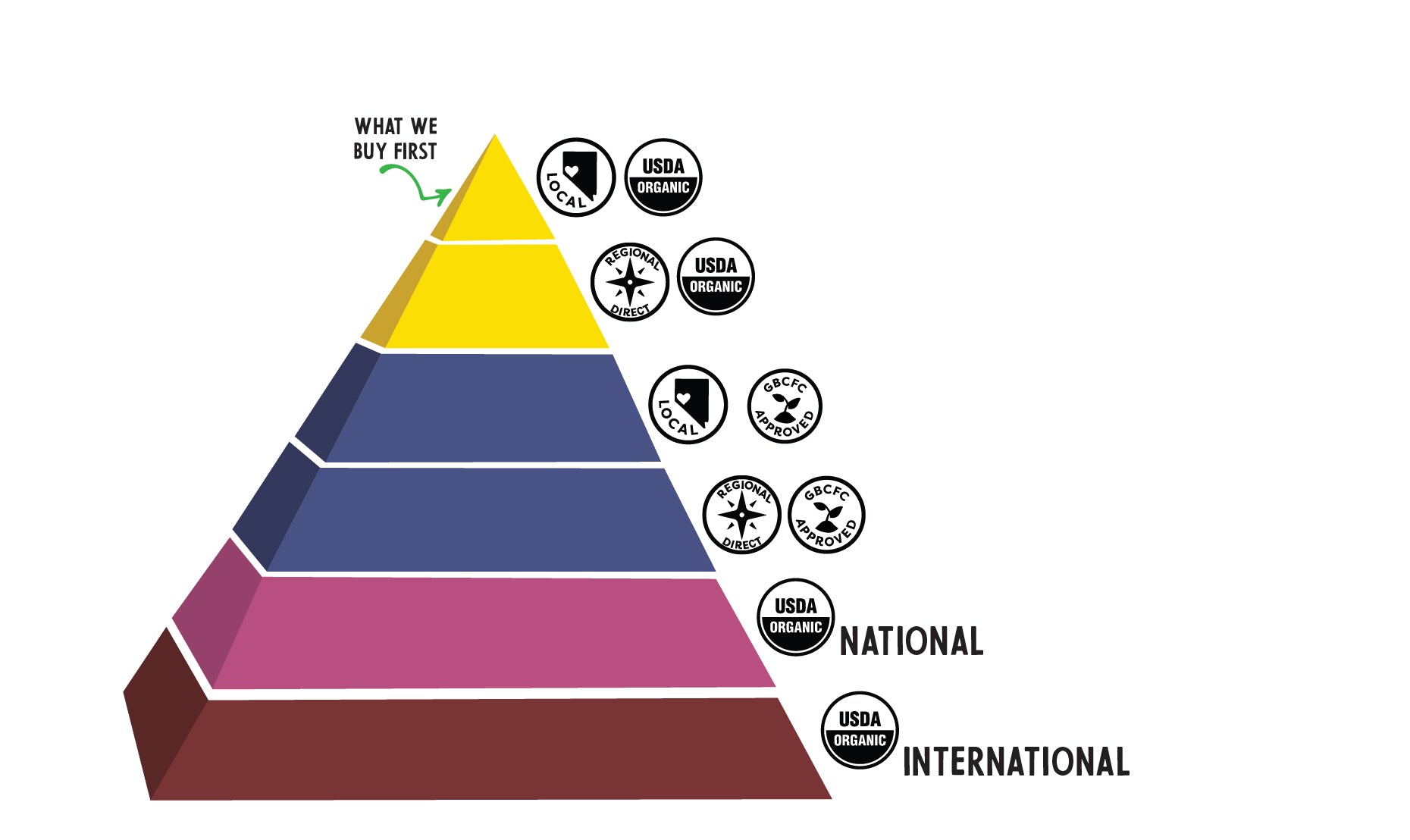
USDA certified organic foods are grown and processed according to federal guidelines addressing soil quality, animal raising practices, pest and weed control, and use of additives. Organic producers rely on natural substances and physical, mechanical, or biologically based farming methods to the fullest extent possible.
Produce can be called organic if it's grown in soil/land that has no prohibited substances applied to it for three years prior to harvest. Prohibited substances include most synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
For meat to get an organic certification, animals must be raised in living conditions accommodating their natural behaviors (like the ability to graze on pasture), fed 100% organic feed and forage, and not administered antibiotics or hormones.When it comes to processed, multi-ingredient foods, the USDA organic standards specify additional considerations. Regulations prohibit organically processed foods from containing artificial preservatives, colors, or flavors and require that their ingredients are organic, with some minor exceptions. For example, processed organic foods may contain some approved non-agricultural ingredients, like enzymes in yogurt, pectin in fruit jams, or baking soda in baked goods.
 Board of Directors
Board of Directors Annual Report
Annual Report Archived E-Letters
Archived E-Letters Contact Us
Contact Us Friends of the Foodshed 501c3
Friends of the Foodshed 501c3 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code